| New Threats Detection Added | • SilentGrabber • Glupteba |
|
Detection Summary
|
|
|
Threat Protections Integrated into Crystal Eye
|
102 |
|
Newly Detected Threats
|
4 |
Weekly Detected Threats
The following threats were added to Crystal Eye this week:
|
Threat name:
|
Silent Grabber | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Silent Grabber is an open source infostealer that is to be used for ‘education only’. The infostealer looks for crypto wallets, system files, Discord info, browser credentials, VPN credentials, several games, and social media accounts.
SilentGrabber also set up persistence on the infected machine while deploying several techniques to bypass EDR detection. It also contains several methods to bypass reverse engineering/ investigation.
The GitHub repo also mentions a new version of SilentGrabber ‘coming soon’ which was posted nearly a year ago. It also mentions that it leaves ‘No Traces and silent’. There is a Discord community where possible development is continuing, and modifications are being made.
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Threat Protected:
|
02 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Rule Set Type:
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Class Type:
|
Trojan-Activity | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Kill Chain:
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Threat name:
|
Glupteba | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Glupteba is a malware that was first seen in the early 2010s and was rated in the top 10 malware list in 2021 and has continued to evolve well into 2025. It utilises the entire infected device, deployed infostealer techniques stealing authentication information, but it can also be used to deploy other malware, and it will enroll the infected machine into a crypto mining botnet.
It has evolved into being able to gain persistence in the UEFI bootloader process, making it extremely difficult to detect and remove.
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Threat Protected:
|
02 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Rule Set Type:
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Class Type:
|
Trojan-activity | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Kill Chain:
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (Week 4 - August 2025)
For more information, please visit the Red Piranha Forum:
https://forum.redpiranha.net/t/known-exploited-vulnerabilities-catalog-3rd-week-of-august-2025/587
|
Vulnerability
|
CVSS
|
Description |
|
Apple iOS, iPadOS, and macOS
|
8.8 (High)
|
Apple iOS, iPadOS and macOS operating systems contain a memory corruption vulnerability that can result in code execution via an out-of-bounds write when processing an image file.
|
|
Trend Micro Apex One
|
9.4 (Critical)
|
Trend Micro Apex One Management Console (on-premise) contains a vulnerability that can allow a remote unauthenticated attacker to execute operating system commands on the device which can result in an attacker gaining access to the system.
|
Updated Malware Signatures (Week 4 - August 2025)
|
Threat
|
Description
|
|
|
XWorm
|
A Remote Access Trojan (RAT) and malware loader that's commonly used in cyberattacks to give attackers full remote control over a victim's system. It's part of a growing trend of commercialised malware sold or rented on dark web forums, often under the guise of a “legitimate tool.”
|
|
|
zgRAT
|
A Remote Access Trojan (RAT) used in cyberattacks that provides attackers with remote access to a machine. Commonly spread in malware loaders and through phishing emails.
|
| Ransomware Report | |
|
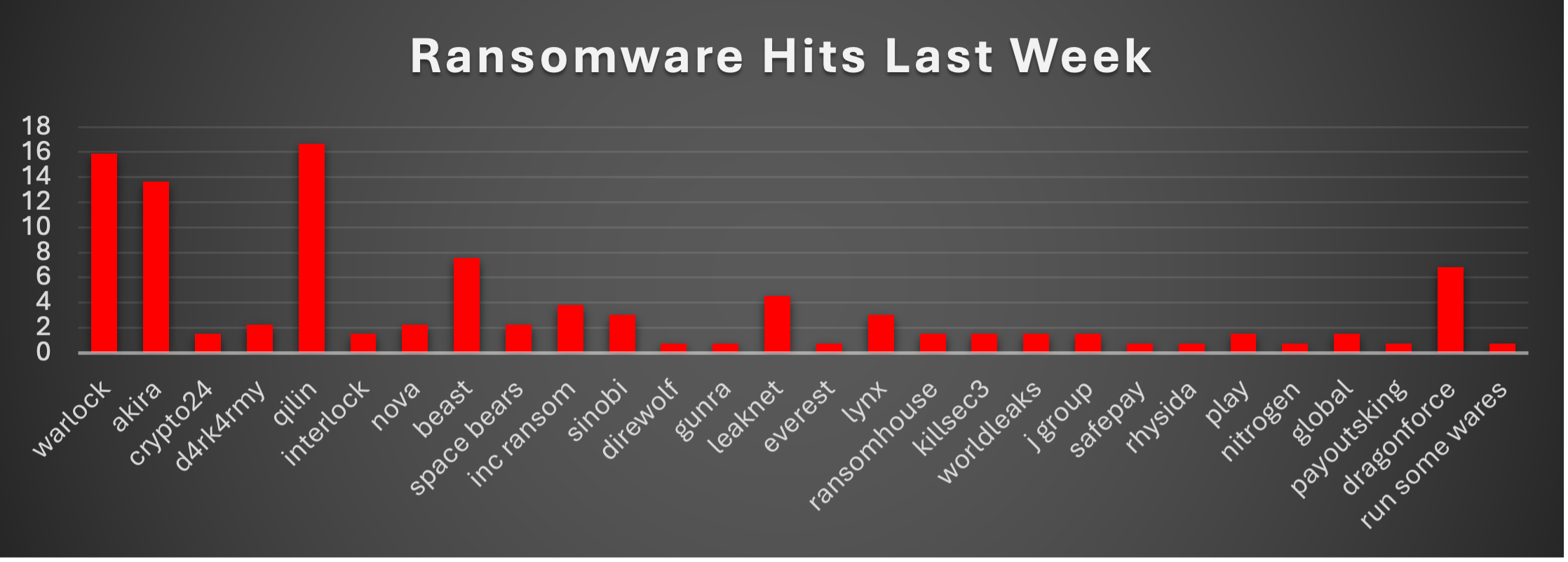
The Red Piranha Team conducts ongoing surveillance of the dark web and other channels to identify global organisations impacted by ransomware attacks. In the past week, our monitoring revealed multiple ransomware incidents across diverse threat groups, underscoring the persistent and widespread nature of these cyber risks. Presented below is a detailed breakdown of ransomware group activities during this period. Ransomware Victims – Weekly Overview Qilin leads this week’s activity with 16.67% of all reported incidents, consolidating its reputation as one of the most aggressive ransomware operators currently active. Its high share reflects ongoing global campaigns and a strong affiliate base. Warlock follows closely at 15.91%, showing a significant surge that suggests targeted campaigns or new tooling being deployed at scale. Akira accounted for 13.64%, maintaining its consistent rise across multiple industries. Its blend of data theft and encryption makes it one of the most disruptive mid-to-top-tier players. DragonForce ranked next with 6.82%, while Beast contributed 7.58%, both demonstrating steady mid-level campaigns targeting a variety of regions and organisations. LeakNet recorded 4.55%, highlighting its sustained operations, while Inc Ransom logged 3.79%, remaining a disruptive force against corporate and enterprise environments. Groups such as Sinobi and Lynx each accounted for 3.03%, while a cluster including D4rk4rmy, Nova, Space Bears, Interlock, RansomHouse, Killsec3, WorldLeaks, J Group, Play, and Global each hovered between 1.52% and 2.27%, demonstrating the breadth of mid-tier operators active this week. Finally, several smaller actors, including Direwolf, Gunra, Everest, SafePay, Rhysida, Nitrogen, PayoutsKing, and Run Some Wares, each represented 0.76% of incidents. While low in volume, these groups reflect the long tail of the ransomware ecosystem, where smaller crews and splinter cells maintain constant opportunistic campaigns. |
LeakNet Ransomware
Executive summary
Red Piranha observed active LeakNet extortion operations on its Tor footprint during this window. The actor’s data-leak site (DLS) and two Tor file servers were enumerated on the group’s page and reachable via mirrors we checked. We also observed multiple new posts dated 2025-08-18 (UTC) and an additional post on 2025-08-21 (UTC), consistent with an ongoing double-extortion cadence (stage data, publish “proof,” escalate with further releases). The group page listed no public chat/admin endpoints, and we found no exposed wallet addresses or countdown timers on the mirrored pages, indicating negotiations are likely handled privately per victim. Across Red Piranha’s checks in this window, we identified no clearnet C2 infrastructure attributable to LeakNet; observable activity was Tor-centric. These findings are based on direct observation of the actor’s page (onion DLS + file servers) and the dated posts within the window.
ATT&CK-mapped TTPs
Initial Access - Valid Accounts (T1078): Typical data-broker crews that leverage purchased/harvested credentials, followed by quiet collection prior to DLS posting. (Pattern-based assessment given LeakNet’s extortion-led posture; no actor-released malware binaries in this window.)
Initial Access - Phishing (T1566): Plausible precursor to mailbox/VPN compromise seen across brokers; no LeakNet-specific kit surfaced this week.
Collection - Email Collection (T1114) & Archive Collected Data (T1560.001): Extortion narratives imply bulk mailbox/share scraping and staging prior to publication. (Consistent with DLS “proof packs”.)
Exfiltration - Exfiltration Over Web Service (T1567): Upload of proof/data to actor-controlled Tor file areas/DLS. Observed infrastructure: DLS + file servers (see IOC section).
Command-and-Control/Comms - Proxy/Anonymity Networks (T1090.003): Public-facing comms via Tor only; no validated clearnet C2 IPs.
Impact - Data Exposure (TA0040/T1657): Primary effect is publication pressure (“direct/double” styles indicated by independent tracker entry).
Impact - (T1486) File Encryption: Not evidenced this week from public materials; LeakNet is consistently tracked as data-broker/extortion first.
MITRE ATT&CK matrix
|
Tactic
|
Technique
|
How it shows up for LeakNet
|
|
Initial Access
|
T1078 Valid Accounts
|
Cred-abuse/IAB hand-off patterns referenced by Mine2
|
|
Initial Access
|
T1566 Phishing
|
Plausible route to mail/VPN
|
|
Collection
|
T1114 Email Collection
|
Mail/file scraping implied by leak themes
|
|
Collection
|
T1560.001 Archive Data
|
Bundled proof & dumps
|
|
Exfiltration
|
T1567 To Web Services
|
Uploads to Tor DLS/file servers
|
|
Exfiltration
|
T1041 Over C2
|
Data moved to onion infra
|
|
C2/Comms
|
T1090.003 Tor
|
DLS nleakk6sejx45jxtk7x6iyt65hwvfrkifc5v7ertdlwm3gttbpvlvxqd.onion
|
|
Impact
|
TA0040 Data Exposure
|
Victim latest posts dated 2025-08-18 (UTC)
|
IOCs
DLS
http://nleakk6sejx45jxtk7x6iyt65hwvfrkifc5v7ertdlwm3gttbpvlvxqd.onion/
File servers
http://ahic5qo3qbjgsyv7x2h5w7uh6nuh45km5srblj7i2amxt57xp4wud2qd.onion/
http://bnlluetsuf6pv7mchgue46h43v66uxtccpg3n5vcdzbeqften5cedlid.onion/
Mitigation with CE 5.0
- Email & Identity: Enforce MFA on VPN/M365/SSO; monitor OAuth grants and inbox-rule creation (T1078/T1114).
- Endpoint/EDR: Heuristics for mass archiving + Tor client execution; detect large share-reads → compression (T1560/T1567).
- Network/Proxy/DNS: Block/alert on .onion in SNI/Host/URI and common tor2web hosts; restrict outbound egress to approved destinations (T1090.003/T1567).
- Backups & DR: Immutable/offline backups; quarterly restore tests for high-value datasets.
Ransomware Victims Worldwide
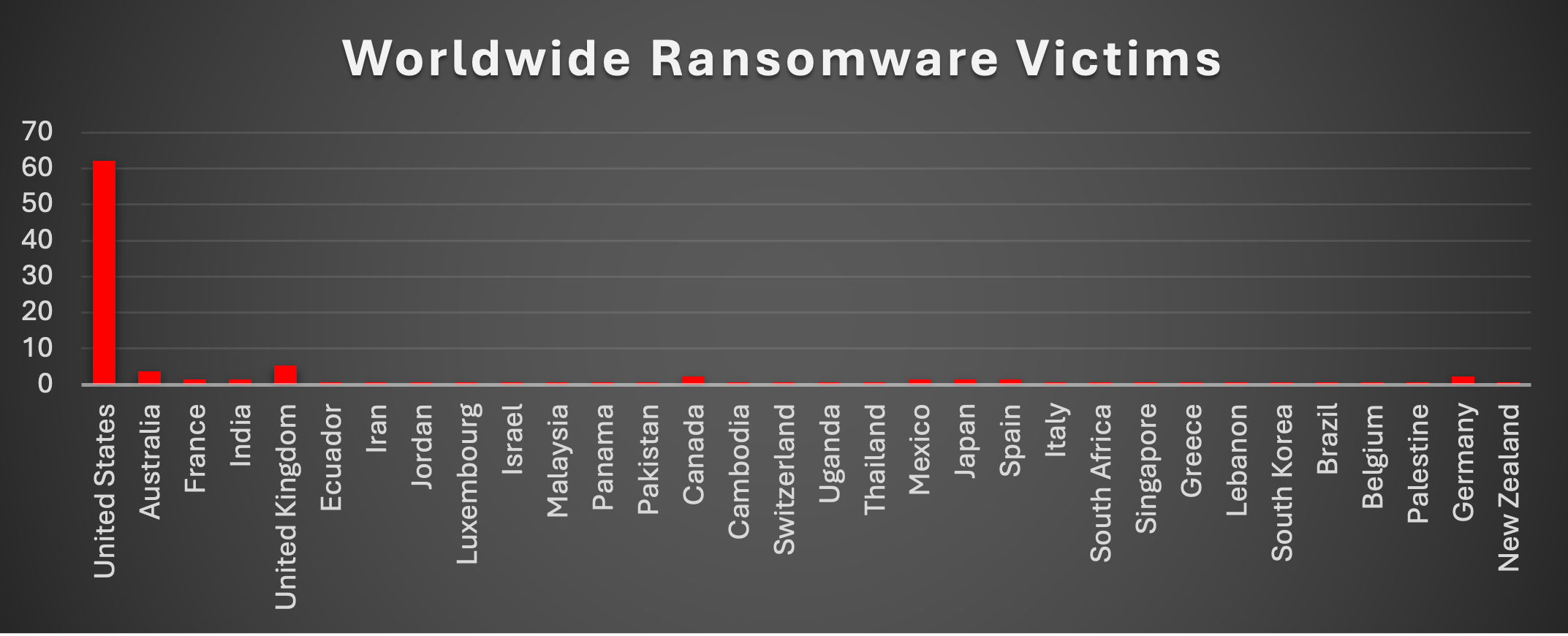
The United States continues to dominate ransomware reporting, with 62.12% of all global incidents this week. Its sheer volume underscores its role as the primary target for ransomware operators, driven by its vast enterprise landscape, critical infrastructure, and relatively higher ransom-paying capacity.
The United Kingdom ranked second with 5.3%, while Australia followed with 3.79%. Both countries remain frequent targets due to their advanced economies, strong digital ecosystems, and deep links to U.S. supply chains.
Canada and Germany each recorded 2.27%, reflecting their vulnerability as highly digitised economies with extensive industrial and financial footprints. France, India, Mexico, Japan, and Spain all logged 1.52% each, reinforcing the broader spread of ransomware activity across both European and Asian markets.
The long tail of nations impacted this week, each reporting 0.76%, includes Ecuador, Iran, Jordan, Luxembourg, Israel, Malaysia, Panama, Pakistan, Cambodia, Switzerland, Uganda, Thailand, Italy, South Africa, Singapore, Greece, Lebanon, South Korea, Brazil, Belgium, Palestine, and New Zealand. These smaller figures emphasise the truly global reach of ransomware, where even less prominent economies continue to experience steady targeting.
Overall, ransomware remains heavily concentrated in North America and Western economies, but opportunistic attacks are being recorded in Latin America, Africa, the Middle East, and Asia-Pacific, underscoring its borderless nature.
Industry-wide Ransomware Victims
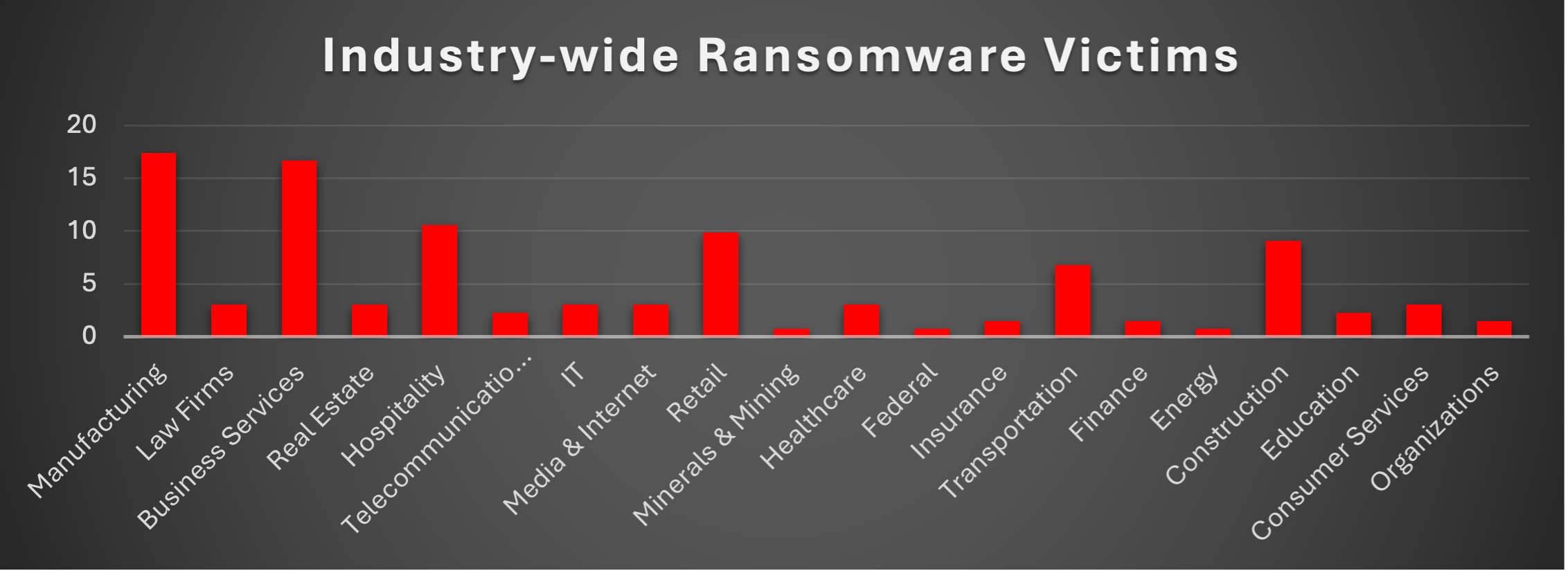
Manufacturing remains the most targeted sector this week, accounting for 17.42% of reported incidents. The reliance on operational technology, supply chain dependencies, and minimal downtime tolerance continues to make this industry a prime target for ransomware operators.
Business Services follow closely at 16.67%, showing consistent exploitation of firms that provide IT, consulting, and outsourcing services. These organisations are especially attractive because compromising them can create indirect access into multiple client environments.
Hospitality logged 10.61%, underscoring ransomware’s steady focus on sectors with guest-facing systems, booking platforms, and sensitive customer data. Construction also reported significant exposure at 9.09%, reflecting vulnerabilities across project-driven environments and decentralised vendor management.
Retail accounted for 9.85%, reaffirming the continued targeting of customer data and payment systems. Transportation saw 6.82%, highlighting the risks posed to logistics and mobility sectors where downtime creates immediate operational disruption.
Law Firms, Real Estate, IT, Media & Internet, Healthcare, and Consumer Services each recorded 3.03%, representing mid-tier targets where data sensitivity and reliance on digital services give ransomware groups leverage during extortion.
Smaller but notable impacts were seen in Telecommunications and Education (2.27% each), while Insurance, Finance, and Organisations followed at 1.52%.
Finally, Minerals & Mining, Federal, and Energy each contributed 0.76%, reinforcing that even highly specialised or critical sectors are not immune from opportunistic attacks.